Title: A Dynamic Wireless EV Charging System with Uniform Coupling Factor and Negligible Power Transfer Fluctuation
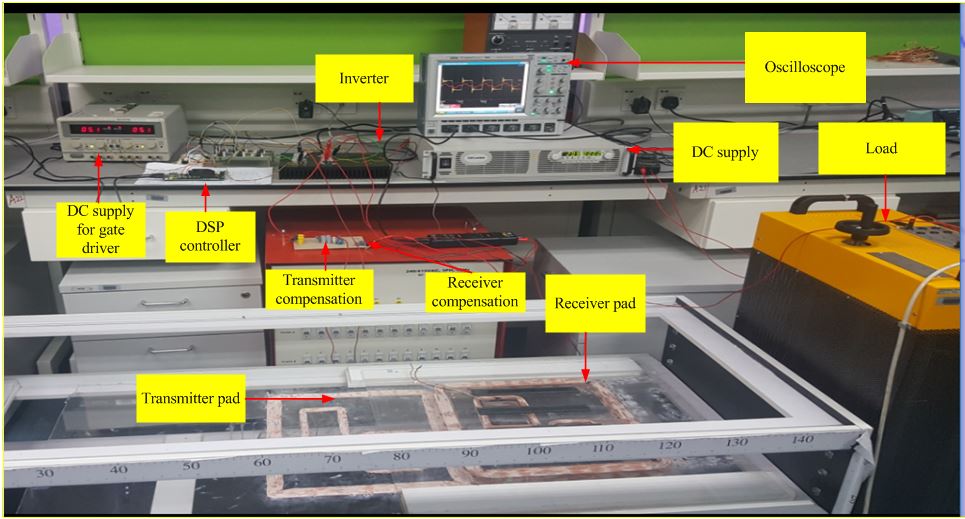
To minimize the dependency on the petroleum products, electric vehicles (EV) have been selected as a feasible solution for transportation purpose. EV was introduced with the appearance of the hybrid electric vehicle (HEV), which causes to bring the development of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). On the other hand, PHEV is responsible for various drawbacks such as the necessity of connecting cables and plug in charger, galvanic isolation of on-board electronics, the weight and size of the charger, and more important safety issues associated with the operation in the rainy and snowing condition. For user friendly and any prevention from the risk by electricity, inductive power transfer (IPT) method has been emerged to charge the EV inductively over the large air gap. There are two types of IPT based EV charging system: stationary and dynamic. High efficiency inductive power transfer (IPT) with low misalignment effect is one of the key issues for dynamic charging electric vehicle (EV) system. This research presents an advanced concept of analysis and design of transmitter and receiver coils with a special arrangement of coil assembly for dynamic charging of EV. In each transmitter coil, large rectangular section is series connected with two zigzag- shaped small rectangular sections. These small sections are back-to-back series connected and located inside the large rectangular section. Adjacent pair of proposed transmitter coil with back-to-back series connection, named as extended DD transmitter is used throughout this paper. One of the contributions of this work is uniform surface magnetic flux distribution, obtained by the zigzag-shaped rectangular sections. Designing of the proposed transmitter and receiver with the simulation results are done by the 2-D finite element analysis (FEA). In case of extended DD transmitter, negligible power transfer fluctuation is the major contribution regardless of the horizontal (x-direction) misalignment of the receiver coil. Justification of the coil design is performed with the load independent voltage gain and power transfer fluctuation characteristics. A compensation technique named LC-LC2 is used in order to obtain the load independent operation and the better tolerance of the air gap variation. Experimental results prove that, power transfer fluctuation with load independent unique voltage gain is within ±6% and efficiency is about 93% under any horizontal (x-direction) misalignment condition of the receiver coil with an air gap of 140mm
Last Update: 22/11/2022